PacketMaze
اللَّهُمَّ إِنِّي أَسْأَلُكَ عِلْمًا نَافِعًا، وَرِزْقًا طَيِّبًا، وَعَمَلًا مُتَقَبَّلًا
Date: 10/8/2025
By: Y0un15
Labs’s link : Link
1-Scenario:
A company’s internal server has been flagged for unusual network activity, with multiple outbound connections to an unknown external IP. Initial analysis suggests possible data exfiltration. Investigate the provided network logs to determine the source and method of compromise.
2. Preliminary Investigation
After opening the PCAPNG file, I began by reviewing its File Properties, Conversations, and Protocol Hierarchy to gain a general overview of the captured traffic.
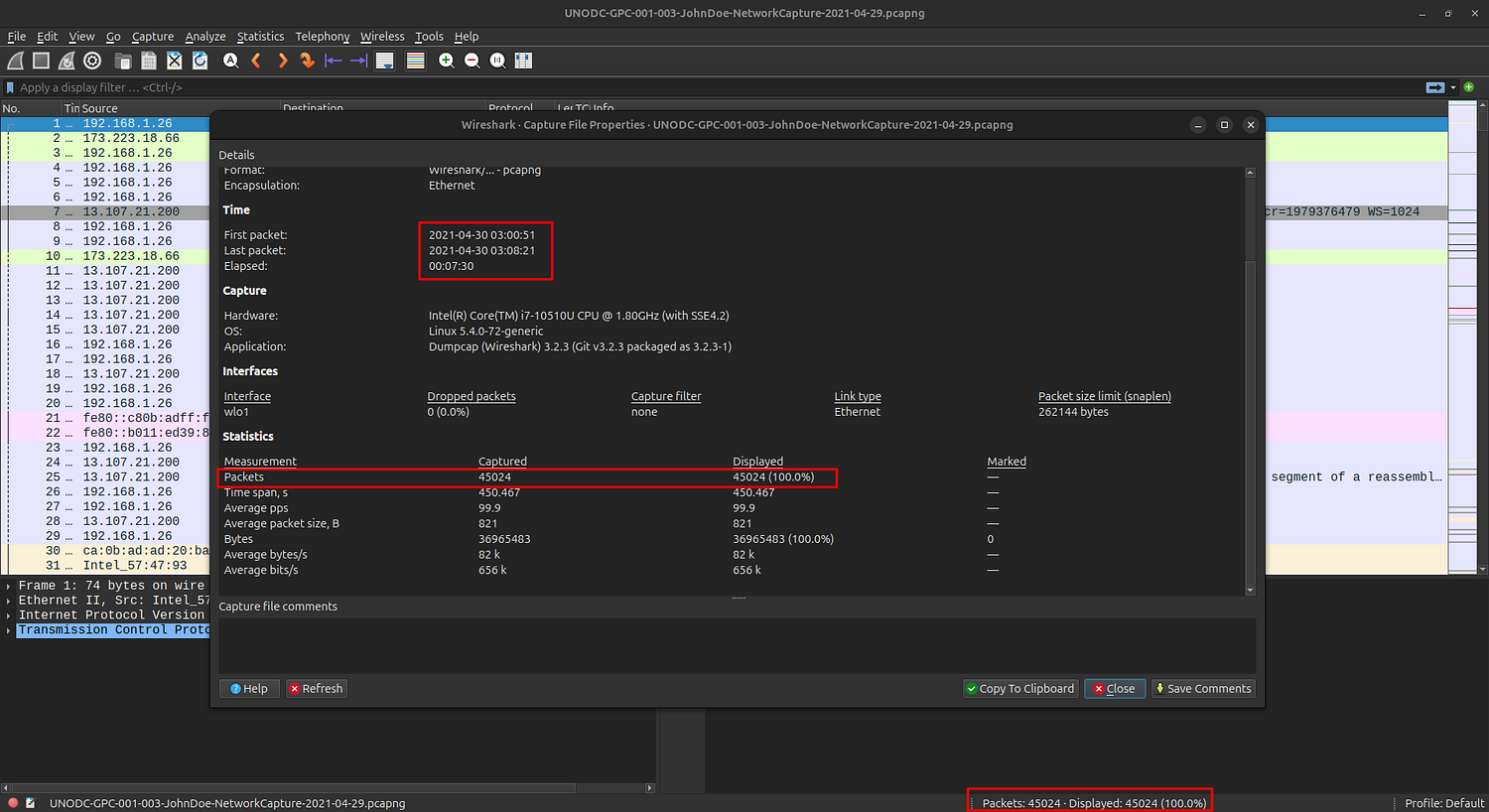
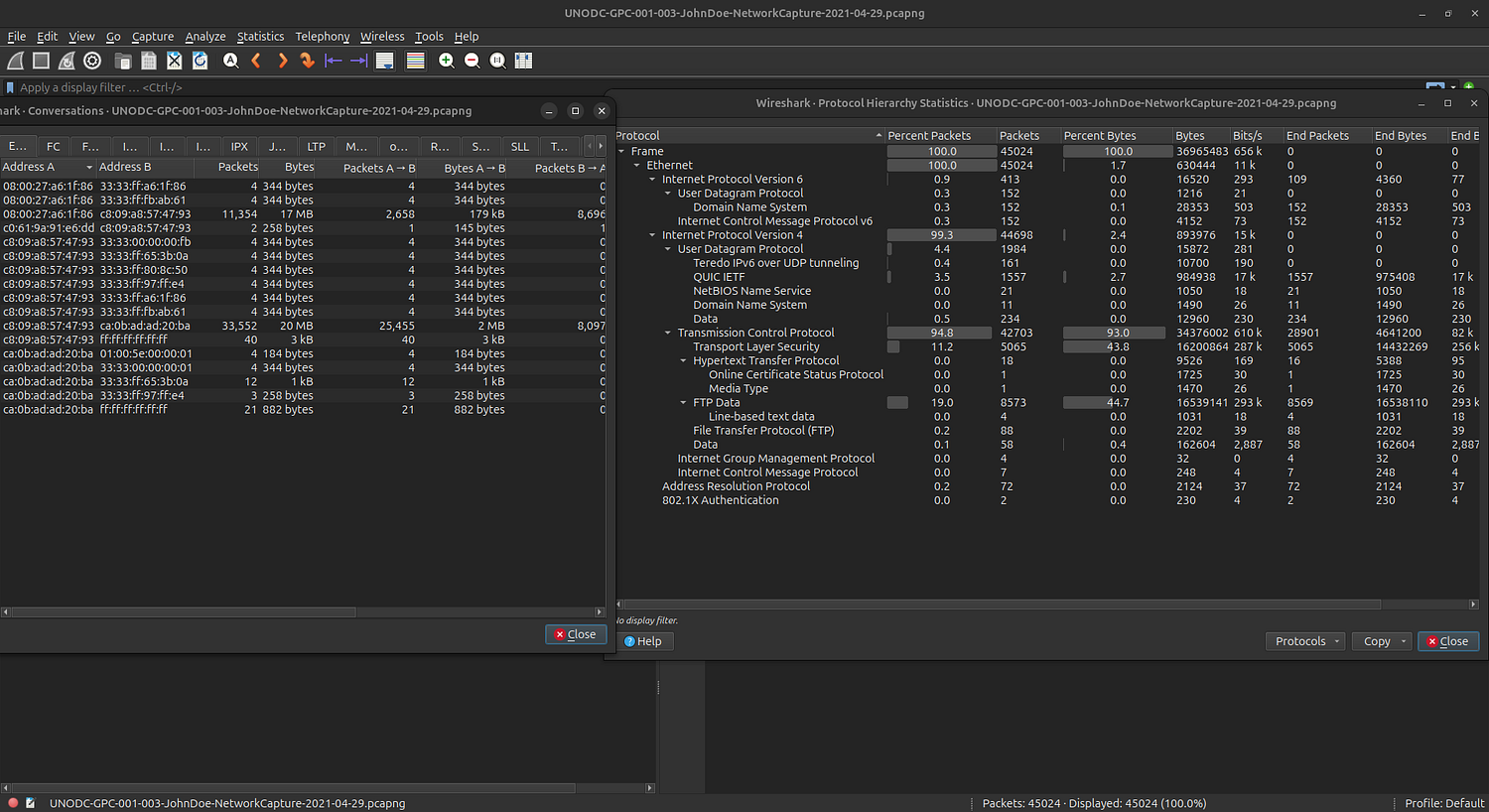
Next, I inspected the Data Objects to extract relevant files — specifically FTP data and HTTP data.
.png)
.png)
3. Challenge Questions:
#What is the FTP password?
#What is the IPv6 address of the DNS server used by 192.168.1.26?
#What domain is the user looking up in packet 15174?
#How many UDP packets were sent from 192.168.1.26 to 24.39.217.246?
#What is the MAC address of the system under investigation in the PCAP file?
#What was the camera model name used to take picture 20210429_152157.jpg?
#What is the ephemeral public key provided by the server during the TLS handshake in the session with the session ID: da4a0000342e4b73459d7360b4bea971cc303ac18d29b99067e46d16cc07f4ff?
#What is the first TLS 1.3 client random that was used to establish a connection with protonmail.com?
#Which country is the manufacturer of the FTP server’s MAC address registered in?
#What time was a non-standard folder created on the FTP server on the 20th of April?
#What URL was visited by the user and connected to the IP address 104.21.89.171?
4-Walking through the Questions :
🔹 Q1 — FTP Password
Filtering for the FTP protocol revealed all related streams. By following one of them, I easily identified the username and password.
.png)
220 Welcome to Hacker FTP service.
AUTH TLS
530 Please login with USER and PASS.
AUTH SSL
530 Please login with USER and PASS.
USER kali
331 Please specify the password.
PASS AfricaCTF2021
230 Login successful.
SYST
215 UNIX Type: L8
FEAT
🔹 Q2 — IPv6 Address of the DNS Server
I filtered packets with DNS, then opened the Conversations tab to identify the DNS servers in use.
.png)
From this image, we can see that I need to find the Ethernet address associated with ID 192.168.1.26 in order to obtain the correct IPv6 address.
By going into any packets above 192.168.1.26, you can find the Ethernet address. After that, you can confirm which one is the correct address (Destination or Source).
.png)
So ip 192.168.1.26 have the address c8:09:a8:57:47:93
Des»c8:09:a8:57:47:93
the DNS traffic from 192.168.1.26 is using the IPv6 address:
fe80::c80b:adff:feaa:1db7
This is the address of the DNS server responding to queries from 192.168.1.26.
.png)
🔹 Q3 — Domain Lookup in Packet 15174
I went to the packet number and followed the stream to reveal the packet and find out what the user was looking for.[I didn’t need to follow the stream]
.png)
🔹 Q4 — UDP Packets Count
To get the packet number, I used this command to filter the packets and select the correct ones that met the conditions.
udp && ip.src==192.168.1.26 && ip.dst==24.39.217.246
.png)
🔹 Q5 — MAC Address of the Investigated System
From the DNS server query, we determined that the server has the MAC address ca:0b:ad:ad:20:ba, and that the IP address 192.168.1.26 has the MAC address c8:09:a8:57:47:93.which is the MAC address to the system under investigation
.png)
🔹 Q6 — Camera Model Name
Through the investigation, I previously found that there was Data object ending in ‘jpg’, which is an image.
.png)
- so after i extract
20210429_152157.jpgand run the exiftool on it i got the camera model
.png)
🔹 Q7 — Ephemeral Public Key from TLS Handshake
using this command to filter for the TLS handshake
tls.handshake.session_id==da4a0000342e4b73459d7360b4bea971cc303ac18d29b99067e46d16cc07f4ff
.png)
#But how to get the public key ?
You can find the key by going to Transport Layer > TLS Handshake Messages > Server Key Exchange.
.png)
🔹 Q8 — First TLS 1.3 Client Random (ProtonMail)
will get us the “Client Hello” message and from that we can find the first TLS client randomYou can find the value in ‘Transport Layer’ > ‘TLSv1.3’ > ‘Handshake Protocol: Client Hello’.
.png)
🔹 Q9 — Manufacturer Country of FTP Server MAC
.png)
(08:00:27:a6:1f:86)
from this img we can see that the client 192.168.1.26 was talking with 192.168.1.20 which is the ip for the server
so the mac for the server is (08:00:27:a6:1f:86)
so using an online MAC lookup you can find from where
.png)
🔹 Q10 — Non-Standard Folder Creation Time
By following the FTP stream, I identified the command indicating a new directory creation on April 20th.
.png)
The image clearly shows that the FTB directory is the intended one, and the time will be 17:53.
🔹 Q11 — URL Visited (Connected to 104.21.89.171)
so we know that the use ip is 192.168.1.26 and the visited ip address is 104.21.89.171 ,so by filtering using those data [ip.src==192.168.1.26 && ip.dst==104.21.89.171]
.png)
- but how can we get the url :)…. it’s obviose that the protocol we need to search in first is “http”…. by filtering using [ip.src==192.168.1.26 && ip.dst==104.21.89.171] and then following the tcp or http stream for the only packet that apperied
.png)
5-Conclusion:
This investigation demonstrates how to identify suspicious activity within network traffic using Wireshark.
By applying targeted filters and analyzing key protocols such as FTP, DNS, HTTP, and TLS, I was able to uncover credentials, trace communication endpoints, extract files, and analyze metadata.
The results confirmed the method of compromise and highlighted the importance of structured, systematic packet analysis in digital forensics.
And that’s all for today’s write-up!
I hope you enjoyed it — see you in the next one! 👋🏻
اللهم انفعنا بما علَّمتنا، وعلِّمنا ما ينفعنا، وزِدنا علمًا وفقهًا وفهمًا